Introduction
GraphRAG is a powerful feature of R2R that allows you to perform graph-based search and retrieval. This guide will walk you through the process of setting it up and running your first queries.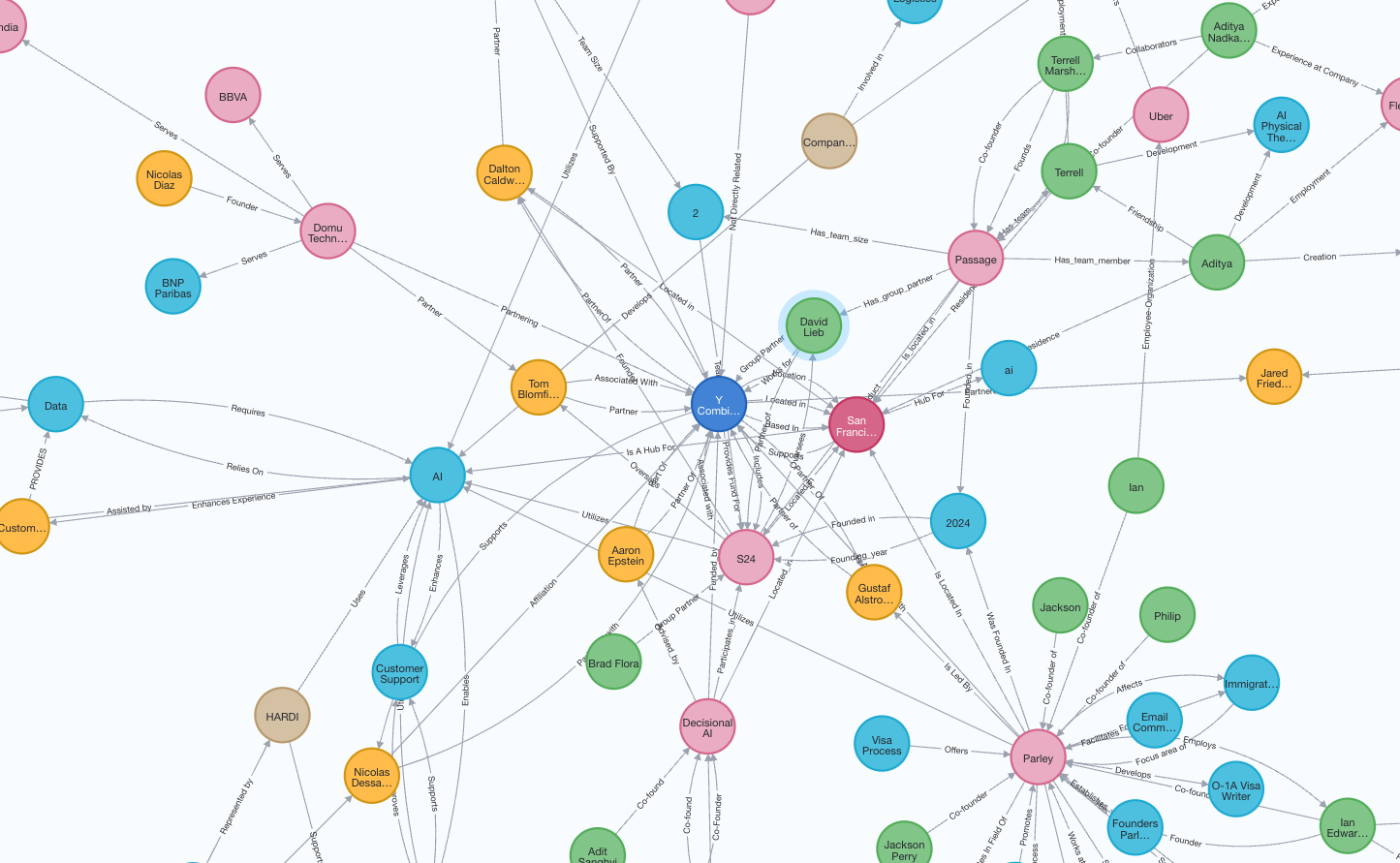
Note that graph construction may take long for local LLMs, we recommend using cloud LLMs for faster results.
Start server
- Cloud LLMs
- Local LLMs
Configuration: r2r.toml
Configuration: r2r.toml
Ingesting files
We begin the cookbook by ingesting the default sample filearistotle.txt used across R2R tutorials and cookbooks:
Example Response
aristotle.txt example file is typically ingested in under 10s. You can confirm ingestion is complete by querying the documents overview table:
Example Response
ingestion_status reads success in the corresponding output.
Create Knowledge Graph
Knowledge graph creation is done in two steps:create-graph: Extracts nodes and relationships from your input document collection.enrich-graph: Enhances the graph structure through clustering and explaining entities (commonly referred to asGraphRAG).
Example Response
Example Response
- Using the
r2r inspect-knowledge-graphcommand.
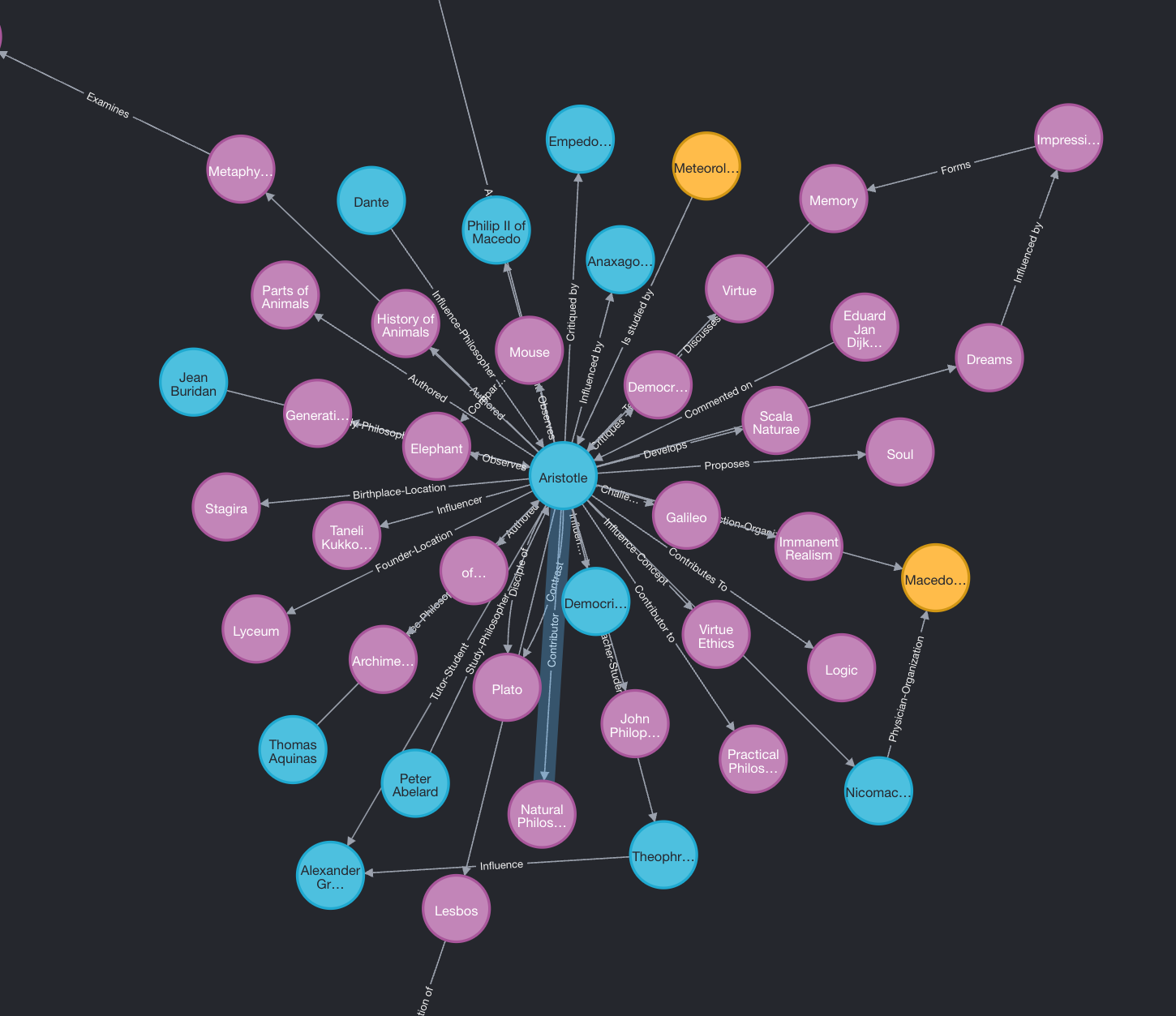
Graph Enrichment
Now we have a graph, but this graph is not searchable yet. We need to perform the graph enrichment step. The graph enrichment step adds node and relationship descriptions, performs hierarchical leiden clustering to create communities, and embeds the descriptions. These embeddings will be used later in the local search stage of the pipeline. If you are more interested in the algorithm, please refer to the blog post here.Example Response
Search
GraphRAG currently supports two types of searches:local and global.
Local search
Local searches are faster and cheaper than global. A local knowledge graph search performs similarity search on the entity, relationship and community description embeddings.Global search
Global searches can be used for queries that require reasoning over the whole dataset. They provide more accurate results, however they use a large amount of queries and are expensive. We recommend checking the number of clusters created in the graph and setting themax-llm-queries to be a fraction (> 0.1) of that number.
global_result from the payload that is returned above we find the following:

